The carrying value of the account is set equal to the total dividend amount declared to shareholders. Dividends Payable is classified as a current liability on the balance sheet, since the expense represents declared payments to shareholders that are generally fulfilled within one year. ABC Limited has 12% cumulative preference shares of $5 million, consisting of 50,000 shares of $100 each. However, the company had declared a 12% dividend for the equity shares this year. Please calculate the dividend payable to the preferred shareholders this year.
Recording Dividend Payments
Investors in DRIPs are able to reinvest any dividends received back into the company’s stock, often at a discount. DRIPs typically aren’t mandatory; investors can choose to receive the dividend in cash instead. The investing information provided on this page is for educational purposes only. NerdWallet, Inc. does not offer advisory or brokerage services, nor does it recommend or advise investors to buy or sell particular stocks, securities or other investments. The dividend payout ratio is the ratio of dividends to net income, and represents the proportion of net income paid out to equity holders.
How a Stock Dividend Works
First Majestic is a publicly traded mining company focused on silver and gold production in Mexico and the United States. The ex-dividend date sets the criteria for eligibility to receive the upcoming dividend. Investors must own the stock before this date to be eligible for the dividend.
Payment Date for Dividends: Overview, Key Dates, and Examples
This would make the following journal entry $150,000—calculated by multiplying 500,000 x 30% x $1—using the par value instead of the market price. If Company X declares a 30% stock dividend instead of 10%, the value assigned to the dividend would be the par value of $1 per share, as it is considered a large stock dividend. This argument has not persuaded the many investors who consider dividends to be an attractive investment incentive. Economists Merton Miller and Franco Modigliani argued that a company’s dividend policy is irrelevant and has no effect on its stock price or its cost of capital.

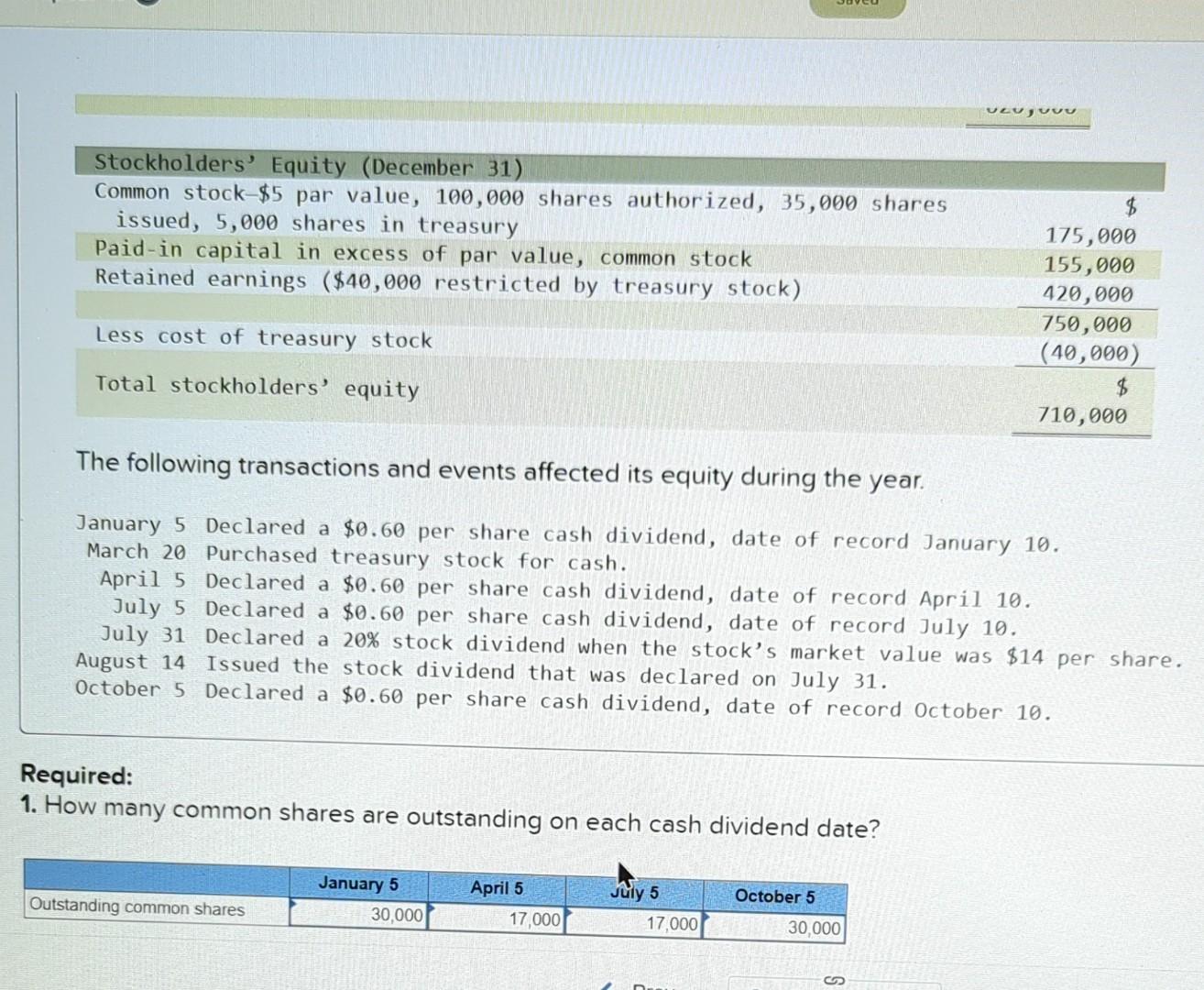
- At the date the board of directors declares dividends, the company can make journal entry by debiting dividends declared account and crediting dividends payable account.
- (2) Telstra is an excellent choice for investors looking to bet on large-cap communication companies.
- These can be key signals in the maturity of your business and optimism of the business owners or directors.
Be sure to check the stock’s dividend payout ratio, or the portion of a company’s net income that goes toward dividend payments. Payout ratios are one measure of dividend health, and they are listed on financial or online broker websites. The debit to the dividends account is not an expense, it is not included in the income statement, and does not affect the net income of the business. The dividends account is a temporary equity account in the balance sheet. The balance on the dividends account is transferred to the retained earnings, it is a distribution of retained earnings to the shareholders not an expense. In addition to dividend yield, another important performance measure to assess the returns generated from a particular investment is the total return factor.
Miller and Modigliani thus conclude that dividends are irrelevant, and investors shouldn’t care about the firm’s dividend policy because they can create their own synthetically. Funds employ the principle of net asset value (NAV), which reflects the valuation of their holdings or the price of the assets that a fund has in its portfolio. The company’s management may have a plan for investing the money in a high-return project that could magnify returns for shareholders in the long run. Thus, in the given question, the company had not declared a dividend for the last two years and declared dividends this year. Cumulative preference shareholders can accumulate the dividend yearly, even though the company has not declared the dividend. As a result, they will receive a dividend for the past years for which the dividend was undeclared in the year of declaration.
In the general ledger hierarchy, it usually nestles under current liabilities. The Board’s declaration includes the date a shareholder must own stock to qualify for the payment along with the date the payments will be issued. GAAP is telling everyone that once dividends are declared, instantly the money is owed. The company is liable for the dividends and you recognize or record the liability. NerdWallet, Inc. is an independent publisher and comparison service, not an investment advisor. Its articles, interactive tools and other content are provided to you for free, as self-help tools and for informational purposes only.
The journal entry does not affect the cash account at this stage, as the actual payment has not yet occurred. When a company issues cash dividends, it is distributing a portion of its profits in the form of cash to its shareholders. The accounting for cash dividends involves reducing the company’s cash balance and retained earnings. The initial declaration entry, as previously discussed, does not affect the cash balance immediately but liability definition does reduce retained earnings to reflect the pending payout. This transaction is straightforward and directly impacts the company’s liquidity, necessitating careful cash flow management to ensure that operational capabilities are not compromised. For example, on March 1, the board of directors of ABC International declares a $1 dividend to the holders of the company’s 150,000 outstanding shares of common stock, to be paid on July 31.
This is explained more fully in our retained earnings statement tutorial. Dividends are a way for companies to distribute profits to their shareholders but not all companies pay dividends. Some may decide to retain their earnings to re-invest in growth opportunities instead. Investors who want to buy shares in companies to receive a recently announced dividend payment have until the day before the ex-dividend or ex-date falls to make their purchase. They won’t appear on the company’s records as shareholders in time to receive the upcoming dividend if they buy on or after the ex-date. For example, if a company issues a stock dividend of 5%, it will pay 0.05 shares for every share owned by a shareholder.
